Exchange Risk Adalah
Exchange risk adalah a pervasive challenge in the realm of international business, where currency fluctuations can have profound implications on companies' financial health. This multifaceted risk arises from the dynamic nature of exchange rates, influenced by a complex interplay of economic, political, and market forces.
Understanding exchange risk is paramount for businesses operating across borders, as it can significantly impact profitability, cash flow, and investment decisions. This article delves into the intricacies of exchange risk, exploring its various types, influencing factors, management strategies, and accounting implications.
Definition of Exchange Risk: Exchange Risk Adalah
Exchange risk, also known as currency risk, arises when a business or individual transacts in a currency other than its own, and the value of the currencies involved fluctuates. These fluctuations can impact the value of assets, liabilities, and cash flows, potentially leading to gains or losses.
For example, if a U.S. company purchases goods from a European supplier and the euro appreciates against the U.S. dollar, the U.S. company will have to pay more dollars to settle the invoice. Conversely, if the euro depreciates, the U.S. company will benefit from a lower cost of goods.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of forex arbitrage.
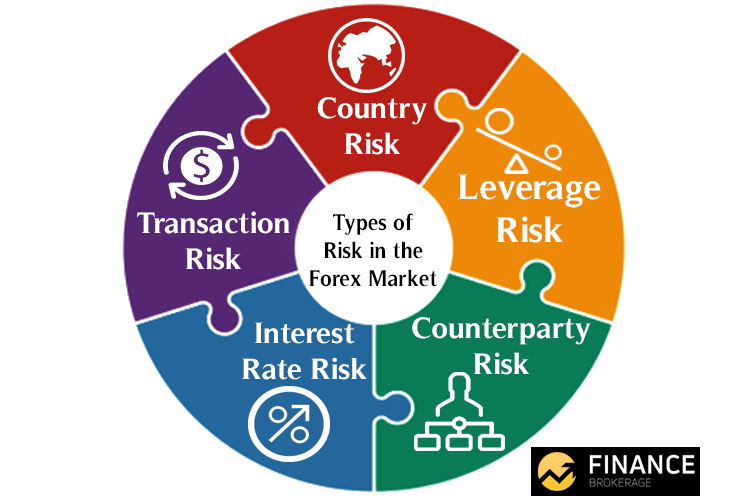
Types of Exchange Risk
There are three main types of exchange risk:
- Transaction risk: Occurs when a transaction is denominated in a foreign currency and settled at a later date, exposing the parties to potential exchange rate fluctuations.
- Translation risk: Arises when a company has foreign subsidiaries and consolidates their financial statements into a single currency. Exchange rate fluctuations can affect the reported value of the subsidiaries' assets and liabilities, leading to translation gains or losses.
- Economic risk: Refers to the broader impact of exchange rate fluctuations on a company's overall financial performance, including its revenue, expenses, and profitability.
Factors Influencing Exchange Risk
Exchange rates are constantly fluctuating, and several factors can influence their movements. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses and individuals exposed to foreign exchange risk.
Investigate the pros of accepting advantages and disadvantages of foreign exchange market class 12 in your business strategies.
Interest Rates
- Higher interest rates in a country tend to attract foreign investment, increasing demand for its currency and appreciating its value.
- Conversely, lower interest rates can lead to currency depreciation as investors seek higher returns elsewhere.
Inflation
- High inflation can erode the purchasing power of a currency, making it less desirable and leading to depreciation.
- Stable or low inflation rates generally support currency value.
Political Stability
- Political instability, such as wars, revolutions, or government changes, can create uncertainty and reduce foreign investment, leading to currency depreciation.
- Stable political environments foster economic growth and attract foreign investment, supporting currency value.
Historical Examples
- In 2008, the collapse of Lehman Brothers triggered a global financial crisis, leading to a sharp depreciation of the US dollar against major currencies.
- In 2016, the Brexit vote caused a significant devaluation of the British pound against the US dollar and other currencies.
Managing Exchange Risk
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/foreignexchangerisk.asp-final2-9472143520d54e5f9ca0d8ea52a4af48.png)
Companies can employ various strategies to manage exchange risk and mitigate its potential impact on their financial performance. These strategies include:
Hedging
Hedging involves entering into financial contracts to offset the risk of exchange rate fluctuations. Common hedging instruments include:
- Forward Contracts: Legally binding agreements to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. They provide certainty in future exchange rates but may limit flexibility in currency management.
- Options: Contracts that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell currencies at a specified rate within a defined period. They offer flexibility but may incur premiums that increase costs.
Case Study: Nike
Nike successfully manages exchange risk through a combination of hedging strategies, including forward contracts and options. By locking in exchange rates for future transactions, Nike reduces the uncertainty associated with currency fluctuations and protects its profit margins.
Impact of Exchange Risk on Business Operations
Exchange rate fluctuations can have a significant impact on business operations, affecting profitability, cash flow, and investment decisions. Companies involved in international trade or with overseas operations are particularly vulnerable to exchange risk.- Profitability: Exchange rate movements can impact a company's profitability by affecting the cost of goods sold, revenue, and operating expenses. For example, a depreciation in the value of the domestic currency against the foreign currency will increase the cost of imported goods and reduce the value of foreign sales, leading to lower profitability.
- Cash Flow: Exchange rate fluctuations can also affect a company's cash flow. A weakening domestic currency can lead to increased costs for businesses that import goods or services from abroad, resulting in reduced cash flow. Similarly, a strengthening domestic currency can reduce the cost of imported goods and increase the value of foreign sales, leading to improved cash flow.
- Investment Decisions: Exchange rate risk can influence investment decisions. A company may postpone or cancel an investment in a foreign country if the exchange rate is expected to move against the domestic currency. Conversely, a favorable exchange rate may encourage investment in foreign markets.
Industries Particularly Vulnerable to Exchange Risk
Industries that are particularly vulnerable to exchange risk include:- Manufacturing: Companies that rely on imported raw materials or components are exposed to exchange risk. A depreciation in the domestic currency can increase the cost of imported materials, leading to lower profitability.
- Retail: Retailers that import goods from abroad are also vulnerable to exchange risk. A depreciation in the domestic currency can increase the cost of imported goods, which may be passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
- Tourism: Exchange rate fluctuations can impact the tourism industry. A strengthening domestic currency can make travel to foreign destinations more expensive, leading to a decline in tourism revenue.
Accounting for Exchange Risk
Exchange risk accounting adheres to the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). These standards guide companies in recognizing, measuring, and disclosing exchange gains and losses resulting from foreign currency transactions and exposures.
Remember to click foreign exchange market long run to understand more comprehensive aspects of the foreign exchange market long run topic.
Methods for Accounting for Exchange Gains and Losses
Companies can account for exchange gains and losses using different methods, including:
- Transaction Method: Records exchange gains and losses when foreign currency transactions occur.
- Translation Method: Adjusts the financial statements of foreign subsidiaries to the parent company's currency, recognizing exchange gains or losses.
- Monetary/Non-Monetary Method: Classifies assets and liabilities as monetary (e.g., cash, accounts receivable) or non-monetary (e.g., inventory, property). Exchange gains or losses are recognized on monetary items only.
Examples of Exchange Risk in Financial Statements, Exchange risk adalah
Exchange risk can impact financial statements in various ways:
- Income Statement: Exchange gains or losses may be reported as separate line items or included in other income or expense categories.
- Balance Sheet: Foreign currency assets and liabilities are translated using exchange rates, leading to revaluation gains or losses.
- Shareholders' Equity: Exchange gains or losses may impact retained earnings and other equity accounts.
Exchange Risk in Emerging Markets
Emerging markets present unique challenges and risks associated with exchange risk due to their developing economies and financial systems. These markets often experience high levels of volatility in their exchange rates, which can significantly impact businesses operating within them.
Factors Contributing to Exchange Rate Volatility in Emerging Markets
- Political and Economic Instability: Political unrest, economic crises, and changes in government policies can lead to fluctuations in exchange rates.
- Currency Speculation: Emerging markets often attract currency speculators who seek to profit from exchange rate movements, leading to increased volatility.
- Dependence on Commodity Exports: Many emerging markets rely heavily on commodity exports, which are subject to global price fluctuations that can affect exchange rates.
- Limited Foreign Exchange Reserves: Emerging markets may have limited foreign exchange reserves to support their currencies, making them more vulnerable to external shocks.
Recommendations for Managing Exchange Risk in Emerging Markets
- Diversification: Businesses should diversify their operations across multiple currencies to reduce the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on any single currency.
- Hedging Strategies: Using financial instruments such as forward contracts, options, or currency swaps can help mitigate exchange rate risk.
- Local Currency Financing: Borrowing in the local currency can reduce the risk of currency devaluation on debt obligations.
- Political and Economic Monitoring: Closely monitoring political and economic developments can help businesses anticipate and prepare for potential exchange rate volatility.
- Risk Management Policies: Establishing clear risk management policies and procedures can help businesses respond effectively to exchange rate fluctuations.
Closing Notes

Exchange risk is an inherent aspect of global commerce, posing both challenges and opportunities for businesses. By comprehending the dynamics of exchange rate fluctuations and implementing appropriate risk management strategies, companies can mitigate potential losses and capitalize on favorable currency movements. Navigating exchange risk effectively is crucial for businesses seeking to thrive in the ever-evolving landscape of international trade.
Comments
Post a Comment