Foreign Exchange Market Definition Ap Macro
Embark on a journey into the realm of foreign exchange market definition AP macro, where currencies dance to the rhythm of global economics. This intricate tapestry of international finance connects businesses, investors, and nations, facilitating seamless cross-border transactions and shaping the very fabric of our interconnected world.
The foreign exchange market, also known as forex, is a vast and dynamic marketplace where currencies are traded 24 hours a day, 5 days a week. It plays a pivotal role in facilitating international trade and investment, allowing businesses to expand their reach, diversify their portfolios, and manage financial risks.
Definition of the Foreign Exchange Market: Foreign Exchange Market Definition Ap Macro
The foreign exchange market, also known as the forex market, is a global decentralized market where currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
Participants in the Forex Market
The forex market involves a wide range of participants, including:
- Banks and other financial institutions
- Corporations and businesses
- Governments and central banks
- Retail traders
Role of the Forex Market in International Trade and Investment
The forex market plays a crucial role in facilitating international trade and investment by:
- Allowing businesses to exchange currencies to pay for goods and services from other countries
- Enabling investors to diversify their portfolios by investing in foreign assets
- Providing a mechanism for governments to manage their exchange rates and foreign reserves
Key Characteristics of the Forex Market
The foreign exchange market, often abbreviated as forex or FX, is characterized by several key features that distinguish it from other financial markets. These characteristics include its over-the-counter nature, 24-hour trading cycle, and high liquidity.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Nature
The forex market is an over-the-counter (OTC) market, meaning that it does not have a centralized exchange where all transactions take place. Instead, forex transactions are conducted directly between two parties, typically through a network of banks and other financial institutions.
The OTC nature of the forex market provides several advantages. It allows for greater flexibility and customization of transactions, as parties can negotiate the terms of their trades directly with each other. It also reduces the risk of market manipulation, as there is no central exchange that can be targeted by manipulators.
Examine how interbank foreign exchange market in kuala lumpur can boost performance in your area.
24-Hour Trading Cycle
The forex market is open 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, making it one of the most accessible financial markets in the world. This is due to the fact that the forex market is a global market, with participants from all over the world. As a result, there is always someone available to trade, regardless of the time of day or night.
The 24-hour trading cycle of the forex market provides several benefits. It allows traders to take advantage of market opportunities at any time of day or night. It also reduces the risk of price gaps, as the market is constantly active.
Enhance your insight with the methods and methods of interbank foreign exchange market news.
High Liquidity
The forex market is one of the most liquid financial markets in the world. This means that there is a large volume of currency available for trading at any given time, making it easy to buy and sell currencies without affecting the price.
The high liquidity of the forex market is due to the large number of participants, including banks, financial institutions, corporations, and individual traders. This ensures that there is always a ready supply of buyers and sellers, which helps to keep prices stable.
Types of Forex Transactions
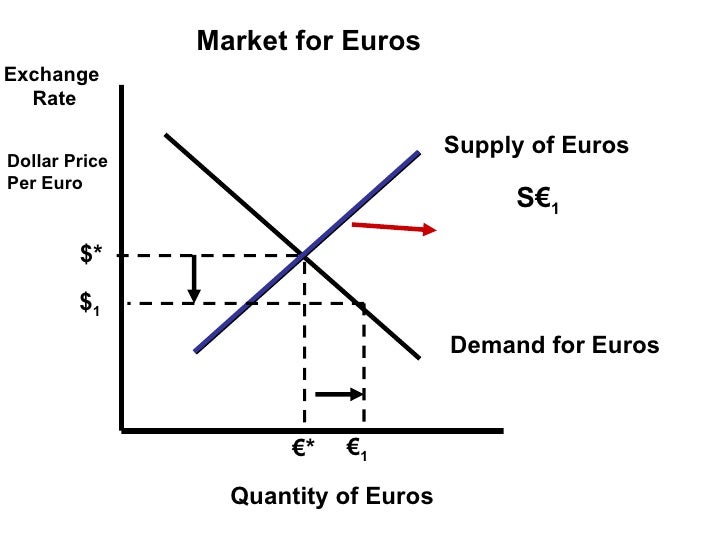
In the foreign exchange market, transactions take on various forms, each serving specific purposes and catering to different needs. Three prominent types of forex transactions include spot transactions, forward transactions, and swaps.
Spot Transactions
Spot transactions are the most straightforward type of forex transaction. They involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate. Settlement typically occurs within two business days. Spot transactions are commonly used for short-term currency trading and to facilitate international payments.
Forward Transactions
Forward transactions, also known as forward contracts, are agreements to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. These contracts allow businesses and individuals to hedge against currency fluctuations and lock in future exchange rates. Settlement occurs on the agreed-upon future date.
Discover more by delving into foreign exchange market pictures further.
Swaps
Swaps are more complex transactions that involve the exchange of not only currencies but also interest rates. Currency swaps allow participants to exchange different currencies while simultaneously exchanging interest payments denominated in those currencies. Interest rate swaps involve the exchange of interest payments between two parties, typically for different currencies or different maturities.
Factors Influencing Forex Rates

The foreign exchange market is influenced by a multitude of economic and political factors that can cause significant fluctuations in exchange rates. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses and investors who engage in international transactions or hold foreign currency assets.
Economic Factors
Economic factors that influence forex rates include:
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth in a country typically leads to an appreciation of its currency, as investors seek to invest in the growing economy.
- Inflation: High inflation can erode the purchasing power of a currency, leading to its depreciation.
- Interest rates: Higher interest rates make a currency more attractive to investors, as they can earn a higher return on their investments.
- Balance of payments: A country with a persistent trade deficit may see its currency depreciate, as there is a greater demand for foreign currency to pay for imports.
Political Factors, Foreign exchange market definition ap macro
Political factors that can impact forex rates include:
- Political stability: Political instability and uncertainty can lead to a depreciation of a currency, as investors become wary of investing in a country with a volatile political environment.
- Government policies: Changes in government policies, such as tax rates or regulations, can affect the attractiveness of a country for investment and trade, impacting its currency's value.
- International relations: Diplomatic tensions or conflicts between countries can lead to a depreciation of the currency of the affected countries.
Supply and Demand
In addition to economic and political factors, supply and demand also play a significant role in determining forex rates. When the demand for a currency exceeds its supply, its value will appreciate. Conversely, when the supply of a currency exceeds the demand, its value will depreciate.
News Events and Central Bank Policies
News events and central bank policies can have a significant impact on forex rates. For example, positive economic news about a country can lead to an appreciation of its currency, while negative news can cause it to depreciate. Similarly, changes in interest rates by central banks can impact the demand for a currency and affect its exchange rate.
Managing Foreign Exchange Risk
Managing foreign exchange risk is crucial for companies and investors operating in a globalized economy. There are various methods to mitigate this risk, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Hedging
Hedging involves using financial instruments to offset potential losses from exchange rate fluctuations. Common hedging strategies include:
- Forward contracts: Binding agreements to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date.
- Currency options: Contracts that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a specified rate.
- Currency swaps: Agreements to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate for a specific period.
Hedging can effectively reduce risk, but it can also limit potential gains if exchange rates move favorably.
Diversification
Diversification involves investing in a variety of currencies to reduce the overall impact of exchange rate fluctuations. This can be achieved through:
- Investing in global assets: Holding assets denominated in different currencies.
- Using currency-hedged funds: Funds that invest in foreign assets while hedging against currency risk.
Diversification can mitigate risk but may result in lower returns compared to concentrated investments.
Example
A multinational company with operations in multiple countries may use a combination of hedging and diversification to manage foreign exchange risk. It could hedge a portion of its exposure using forward contracts while diversifying its investments by holding assets in different currencies.
Last Recap
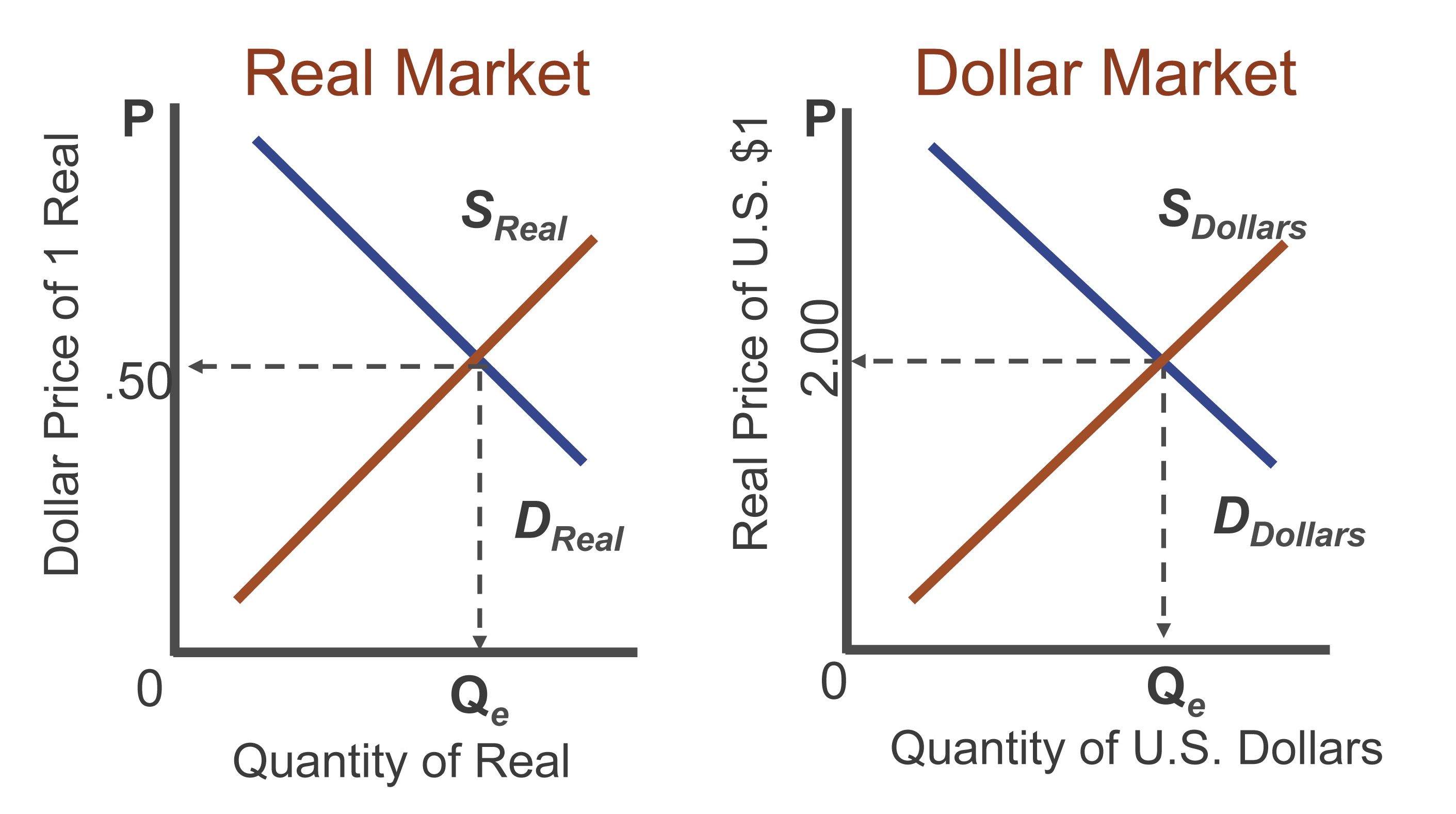
As we conclude our exploration of foreign exchange market definition AP macro, it becomes evident that this complex and ever-evolving ecosystem is a cornerstone of global commerce. Its impact extends far beyond currency exchange, influencing economic growth, investment decisions, and the stability of financial markets worldwide.
Understanding the intricacies of the foreign exchange market empowers businesses, investors, and policymakers to navigate the complexities of international finance, mitigate risks, and seize opportunities in an interconnected global economy.
Comments
Post a Comment